
Sycamore (Acer pseudoplatanus)
Also known as: Great maple, Plane maple, Lock-and-key-tree
Sycamore wood, derived from the sycamore maple (Acer pseudoplatanus), is prized for its versatility and aesthetic qualities. It is widely utilized in the creation of furniture, cabinetry, and veneers due to its appealing grain and smooth texture. Additionally, sycamore wood is ideal for making musical instruments, wooden flooring, and various kitchen utensils such as cutting boards and butcher blocks. Its durability and ease of use make it a popular choice for numerous woodworking applications.
Attributes of Sycamore
Images of Sycamore


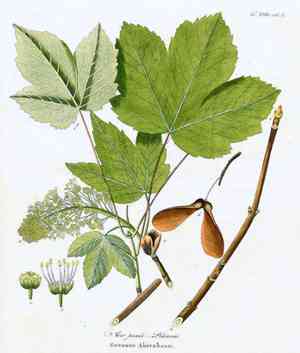

Quickly Identify Sycamore
Scientific Classification of Sycamore
Planting and Growing of Sycamore
 How to Water Sycamore?
How to Water Sycamore?
 What Are the Sunlight Requirements for Sycamore?
What Are the Sunlight Requirements for Sycamore?
 What Is the Ideal Temperature Range for Sycamore?
What Is the Ideal Temperature Range for Sycamore?
 What Soil is Best for Sycamore?
What Soil is Best for Sycamore?
 How to Fertilize Sycamore?
How to Fertilize Sycamore?
 How to Prune Sycamore?
How to Prune Sycamore?
 How to Propagate Sycamore plant?
How to Propagate Sycamore plant?
 How to Repot Sycamore plant?
How to Repot Sycamore plant?
Toxicity of Sycamore
Is Sycamore toxic to humans?
Sycamore presents a mild toxicity risk to humans when ingested. Every part of this plant is deemed toxic and can result in poisoning if eaten. The toxic characteristics are largely attributed to the presence of hypoglycin A (HGA) and pyrogallol. Upon ingestion, individuals may suffer from various symptoms, not limited to gastrointestinal issues such as nausea and vomiting, as well as weakness and hypoglycemia due to hypoglycin A. The intensity of symptoms can differ depending on the quantity consumed and the individual's sensitivity. People should be mindful of the possible dangers linked to the unintentional consumption of any sycamore part, particularly because the whole plant contains toxic compounds.
Is Sycamore toxic to cat?
The Sycamore tree has been recognized to exhibit a mild level of toxicity to cats. Felines might inadvertently consume various parts of the sycamore, and it is crucial to understand that every part of the plant is harmful. Ingesting sycamore can result in symptoms that indicate physical discomfort, illness, or pain. Two toxic compounds identified within sycamore are hypoglycin A (HGA) and gallic acid, which contribute to its poisonous characteristics. Considering these dangers, cat owners are advised to observe their pets for any abnormal behavior and promptly seek veterinary assistance if poisoning is feared.
Is Sycamore toxic to dog?
Sycamore is regarded as having mild toxicity for dogs. If canines inadvertently consume this plant, it may lead to poisoning. All parts of the plant, including its leaves, seeds, and bark, harbor toxic compounds that pose a risk to a dog's well-being. Upon ingesting sycamore, a dog could show signs such as vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, or lethargy. It is vital for dog owners to remain alert and keep their pets away from areas where sycamore is present. Should a dog accidentally consume sycamore, it is essential to seek prompt veterinary assistance to ensure the best possible care for the animal.













